|
|
 |
|
Effects of Champex, as proven by In-Vitro and In-Vivo tests
Section Four - Improvement of Evacuation and Faecal Quality.
4-1 - The control effect on the progression of chronic renal failure patient
In persons suffering from renal failure, the excretory function of harmful chemicals generated by body wastes declines. As a result, the patient would begin to show signs of uremia through the accumulation of injurious chemicals in the blood. As renal failure advances and reaches an advanced stage, the patient exhibits headaches, nausea and other critical symptoms. At present, hemodialysis is used on patients to artificially and continuously filter out injurious chemicals in the blood or kidney transfer is introduced where applicable. Dietary treatments are also introduced, restricting protein intake to reduce these chemicals in the blood.
Dr. T. Sanaka, associated professor, Composite Medical Treatment Center for Renal Disorders, Tokyo Women's College, found that when Champex was administered to non-dialyzed patients suffering renal insufficiency, their renal functions showed a remarkable improvement, to an extent that the application of hemodialysis could be avoided. The results of his first 3 cases are summarized below,
Case 1
Patient is a 67 years old male suffering from chronic renal insufficiency caused by a contracted kidney. Dietary treatments had been introduced to restrict protein intake to 50 grams with 2200 kcal of energy per day. Following continuous administration of Champex at 500mg per day, the serum creatinine level showed a continuous decline from 1.95 mg/dl to 1.69 mg/dl at 4.5 months of Champex administration.
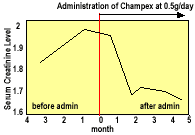
Case 2
Patient is a 40 years old female suffering from chronic renal failure caused by Mensangium cell proliferative glomerulonephritis and complicated with hypertension. Dietary treatments had been introduced to restrict protein intake to 25 grams with 2100 kcal of energy per day.
|
The kidney function had been maintained at levels of 6.2 to 6.7 mg/dl of serum creatinine for a period of 5 months through dietary treatments. After oral administration of Champex at 0.5 to 1 gram per day was introduced, the serum creatinine level declined to 5 mg/dl. When the administration of Champex was discontinued, the serum creatinine levels showed an upward trend but they started to decline again when Champex administration was resumed.
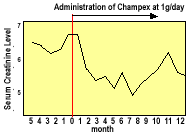
Case 3
Patient is a 24 years old male suffering from chronic renal failure caused by Mesangium cell proliferative glomerulonephritis and complicated by hypertension. Dietary treatments were introduced to restrict protein intake to 25 grams with 2200 kcal of energy per day. The administration of 0.5 to 1 gram per day of Champex was initiated when his kidney function measured a serum creatinine level of 3.66 mg/dl. An increase of the creatinine level was suspended and a level of 3.5 mg/dl was maintained after 6 months of administering Champex.
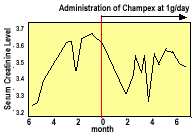
As illustrated above, the results clearly indicate that continuous administration of Champex at 0.5 to 1 gram per day control the serum creatinine level, delaying the progress of chronic renal failure.
|
4-2 - Suppression of leucotriene (allergic substance)
Leucotriene is an allergic substance mainly generated during the onset of bronchial asthma. The suppressive effect of Champex on leucotriene was measured using rat abdominal mast cells in comparison with hydrocortisone, a steroid chemical. As shown in the table 1, Champex at levels as low as 5 mcg shows a highly suppressive effect against 4 types of leucotrienes.
Table 1.
Suppressive percent of CHAMPEX against leucotrienes in rat abdominal mast cells
|
| Test Materials | LTB. | LTC. | LTD. | LTE. |
| CHAMPEX (g/mg) | | | | |
| 0.05 | 16.9 | 10.6 | 22.5 | 25.8 |
| 0.5 | 22.9 | 21.2 | 44.8 | 42.4 |
| 5 | 46.9 | 22.2 | 52.3 | 52.5 |
| 50 | 78.2 | 53.3 | 76.6 | 72.6 |
| 500 | 90.0 | 65.8 | 84.8 | 88.3 |
| Hydrocortisone | 72.5 | 70.1 | 62.5 | 70.5 |
|
4-3 - Eliminating effect of Champex on active oxygen
Active oxygen is known to promote aging and cause various diseases when generated in large quantities in our body. In the case of ischemic disease, for example, a considerable volume of active oxygen is discharged in the affected part by the xanthine oxidase that is generated in our body. As indicated in the table, however, Champex is able to eliminate 50% of active oxygen at 10 micrograms that is very low concentration.
Blocking Effect of CHAMPEX on Active Oxygen
|
| CHAMPEX (g/mg) | Blocking Rate
(%) |
| 1 | 37 |
| 3 | 44 |
| 10 | 51 |
| 30 | 78 |
| 100 | 83 |
|
| |
|
|